, journal entries are the initial step in recording financial transactions. A journal entry involves debiting one or more accounts and crediting one or more accounts in accordance with the golden rules of accounting. These rules ensure that each transaction is recorded correctly and the accounting equation remains balanced.
1. Golden Rules of Accounting
The golden rules of accounting are the foundation of double-entry bookkeeping and the basic principles that form the foundation of the accounting process. These rules guide accountants in recording financial transactions accurately and consistently, these rules govern how to debit and credit accounts when recording a transaction. There are three primary golden rules:

Transactions for Journal Entries
Now, let’s consider 10 transactions that a business might encounter. For each
transaction, we will apply the golden rules of accounting to make journal entries.
- Purchased goods worth ₹1,000 in cash.
- Sold goods worth ₹2,000 on credit to Mr. John.
- Paid rent of ₹500 in cash.
- Received ₹1,200 from Mr. John.
- Purchased equipment worth ₹5,000 on credit.
- Paid salaries of ₹1,000 in cash.
- Borrowed ₹2,000 from the bank.
- Sold goods worth ₹1,500 for cash.
- Paid ₹300 for electricity bill in cash.
- Owner invested ₹10,000 in the business
Journal Entries for the Transactions
Let’s now make journal entries for each of these transactions, applying the golden rules of accounting.
1. Purchased goods worth ₹1,000 in cash.
Real Account: Debit goods (what comes in).
Cash Account: Credit cash (what goes out).

2. Sold goods worth ₹2,000 on credit to Mr. John.
Real Account: Credit goods (what goes out).
Personal Account (Mr. John): Debit the receiver (Mr. John).

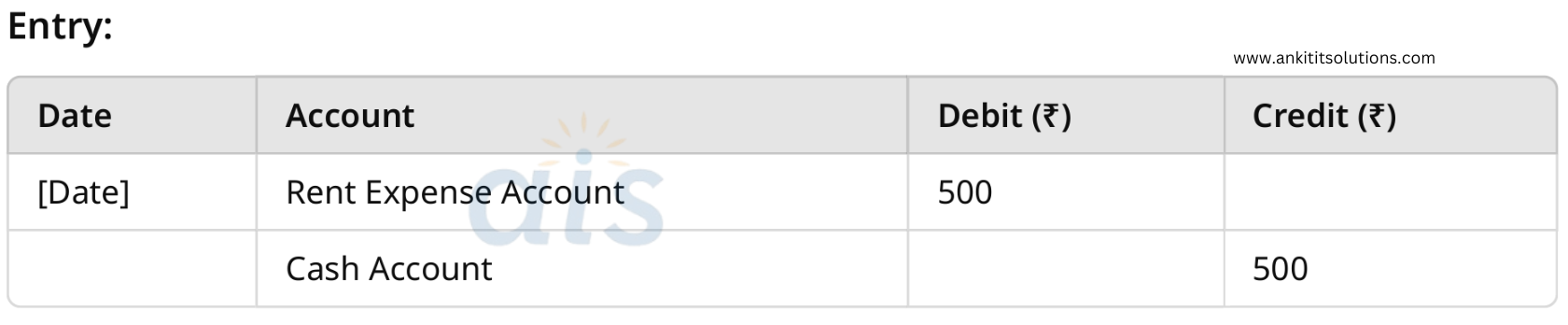
3. Paid rent of ₹500 in cash.
Nominal Account: Debit rent expense (all expenses are debited).
Cash Account: Credit cash (what goes out).
4. Received ₹1,200 from Mr. John.
Personal Account (Mr. John): Credit the giver (Mr. John).
Cash Account: Debit cash (what comes in).

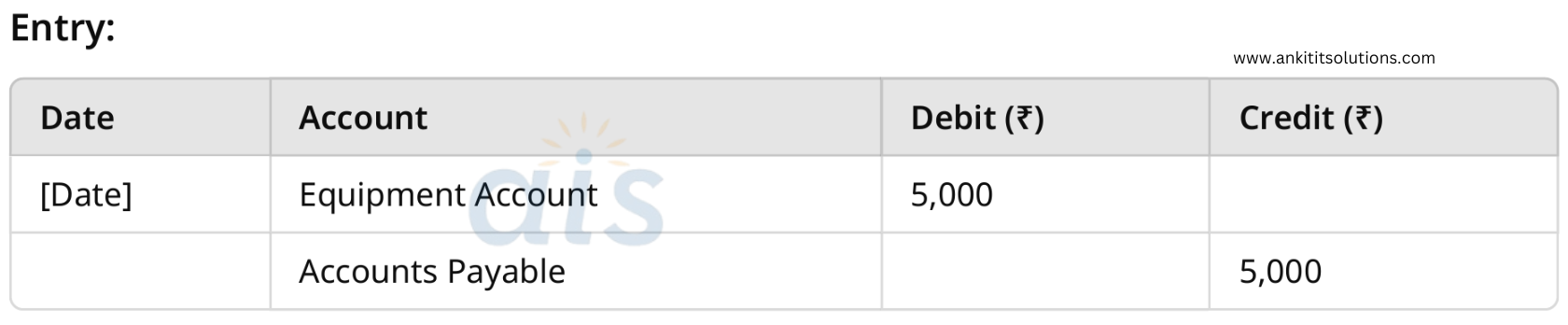
5. Purchased equipment worth ₹5,000 on credit.
Real Account: Debit equipment (what comes in).
Liabilities Account: Credit accounts payable (credit purchase).
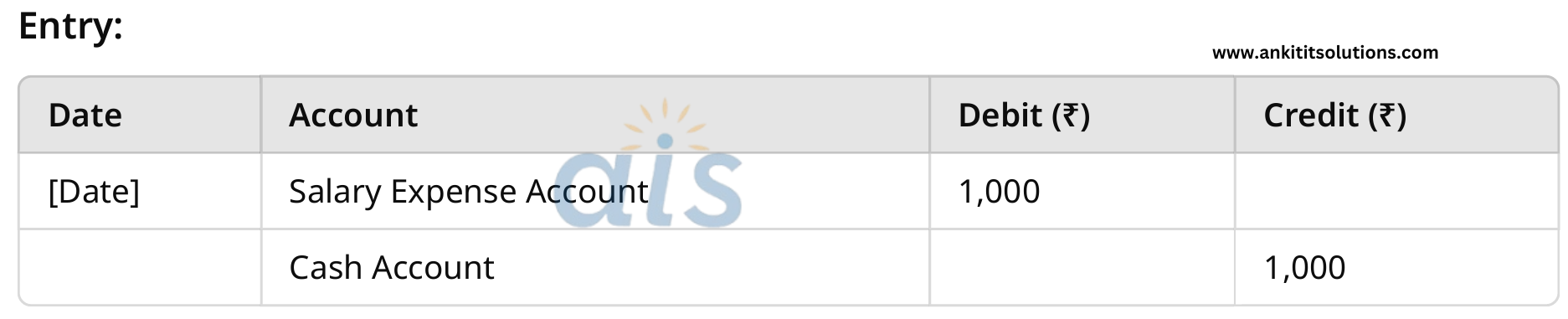
6. Paid salaries of ₹1,000 in cash.
Nominal Account: Debit salary expense (all expenses are debited).
Cash Account: Credit cash (what goes out).
7. Borrowed ₹2,000 from the bank.
Liabilities Account (Bank Loan): Credit the giver (bank).
Cash Account: Debit cash (what comes in).

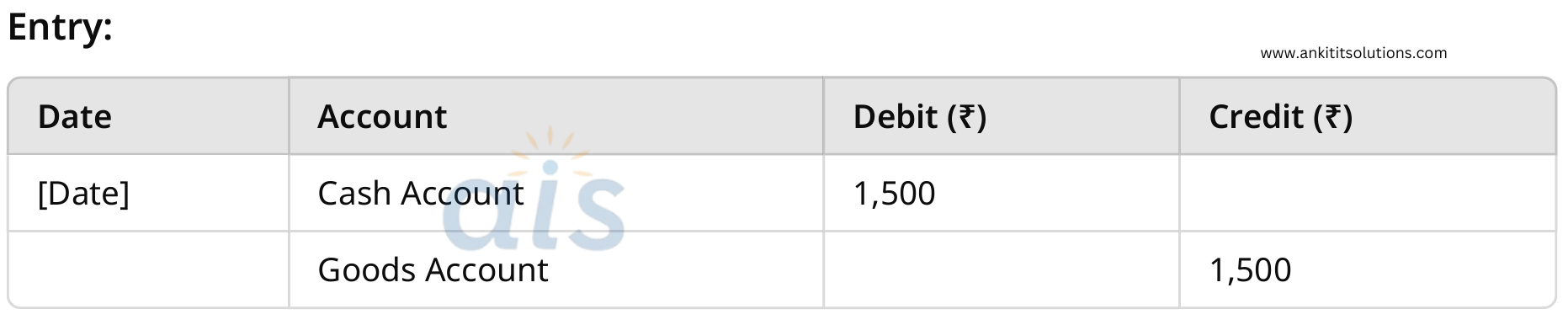
8. Sold goods worth ₹1,500 for cash.
Real Account: Credit goods (what goes out).
Cash Account: Debit cash (what comes in).
9. Paid ₹300 for electricity bill in cash.
Nominal Account: Debit electricity expense (all expenses are debited).
Cash Account: Credit cash (what goes out).

10. Owner invested ₹10,000 in the business.
Personal Account (Owner): Credit the giver (owner).
Capital Account (Equity): Debit the receiver (business).

Effect of Journal Entries
The effect of these journal entries can be observed in the following table, showing how each transaction affects the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity):

By applying these rules to various transactions, students can ensure that all entries are recorded correctly, and the accounting equation remains balanced. TallyPrime helps automate this process, making it easier to maintain accurate and efficient financial records.
Another Example
1. Mr. Sachin started Business with Cash of Rs. 1,00,000.
Assignment
12. Received Cash from Sanjay of Rs. 10000.
14. Paid Rent Expenses of Rs. 3000 by Cash.
15. Purchase goods of Rs. 10,000 by Cash.
16. Paid Cash to Krishna of Rs. 7000.
17. Received Commission of Rs. 5000 by Cash.
18. Paid petrol Expenses of Rs. 300 by Cash.
19. Loan taken(Receipt) from Bhushan of Rs. 20,000 in cash.
20. Sold goods to Jayesh Agencies of Rs. 17000 on credit.
21. Received cheque from Sanjay of Rs. 2000.
22. Deposited Cash in HDFC Bank of Rs. 10,000.
23. Paid Office Expenses of Rs. 500 by Cash.
24. Paid Electricity Expenses by cheque of Rs. 1000.
25. Cheque of Rs. 1500 transfered from HDFC Bank to ICICI Bank .
26. Purchased AC from Mahavir Enterprises of Rs. 10,000 on Credit .
27. Received Cash From Jayesh Agencies of Rs. 1500 .
28. Paid Octroi Expenses of Rs. 400 Cash.
29. Sold goods of Rs.15000 on Cash.
30. Purchased goods of Rs. 3000 by Cash.
Example 2
Create Company with following details:
Suresh Pvt Ldt
206, J B Patel Road, Kandivali (West) Mumbai-400042.
1. Company. Has Opening Cash Rs. 2, 00,000/-
2. Company. Purchase Building of Rs. 5, 00,000/- in cash.
3. Company. Purchase Plant & Machinery cash of Rs. 5, 00,000/-
4. Company. Purchase One Nano Car on Tata Motor’s ltd. Rs. 1, 25,000/-
5. Company. Cash paid to Tata Motor’s ltd. Rs. 1, 25,000/-
6. Deprecation on Building is of Rs. 5,000/-
7. Company. Purchase Passion Plus on cash Rs.48, 000/-
8. Company. Purchase Furniture on cash Rs.18, 000/-
9. Company. Purchase Laptop on cash Rs.45, 000/-
10. Depreciation on Laptop is of Rs. 450/-
11. Depreciation on Furniture is of Rs. 1,800/-
12. Company. Purchase Air Condition of Rs. 30,000/- in cash.
13. Depreciation on Air Condition is of Rs.300/-
14. Company. Purchase Motorola Mobile Rs. 9,850/- in Cash.
15. Depreciation on Plant & Machinery is of Rs. 5,000/-
16. Company. Sales to Mukesh & Son’s Rs. 50,000/-
17. Company. Sales to Mahi & Com Rs. 5, 00,000/-
18. Company. Sales to Mustafa & Brother’s Rs.1, 50,000/-
19. Company. Sales to Arjun & Son’s Rs. 80,000/-
20. Company. Received from Mukesh & Son’s Rs. 43,000/-
21. Company. Received from Mahi & Com. Rs. 3, 50,000/-
22. Company. Received from Mustafa & Brother’s Rs. 1, 20,000/-.
23. Company. Received from Arjun & Son’s Rs. 50,000/-
Answer: – Net Profit 767450/-
Example 3
Create Company with following details:
Atul & Company,
Shop No 2304,
Station Road Next to City Mall, Mumbai Central East, Mumbai-400028.
1 Sales to P.S. Enterprises Rs. 10,000/-
2 Purchase JBL Shares from Kumar Expert’s Rs. 1, 00,000/-
3 Paid Electricity bill Rs.15, 000/- in Cash.
4 Paid to Vishwas Worker Rs.10, 000/- as a Loan in cash.
5 Purchase furniture from Calvin Art (on credit) Rs. 80,000/-
6 Purchase Building Rs. from Shree Ram Financer Rs. 5, 00,000/-
7 Sales One Hero Honda bike to Mohan Sharma Rs. 20,000/-
8 Receive Mr. Ram Lal & sons by cash 1, 00,000/-
9 Pay to Mr. Mukesh & Son’s. Rs. 15,000/-
10 Purchase Computer from Krishna Computer’s Rs. 45,000/-
11 Receive to Ps Enterprises Rs. 10,000/- in Cash.
12 Paid to Kumar Expert’s Rs. 1, 00,000/- in cash.
13 Received from Vishwas worker Rs. 10,000/- in cash.
14 Paid to Calvin Art Rs. 80,000/- in Cash.
15 Paid to Shree Ram Financer Rs. 5,00,000/- in Cash.
Answer: – Net Loss 85,000/-
Example 4
Create Company with following details
Mahima Electronics, 124, S.V. Road, Mulund (W), Mumbai-400097.
1. Company. has toward bank Account’s (A) HDFC Bank – 50,000/- (B) ICICI Bank -70,000/-
2. Company. Has Opening Cash – 1, 00,000/-.
3. Company. Deposited cash in to HDFC Bank – 15,000/-
4. Company. Deposited cash in to ICICI Bank -10,000/-.
5. Company. Purchase a Nokia Mobile N-73 of Rs. 13,400/- from Abhishek Mobile World.
6. Company. Purchase from Kanak Agency A Cooler Rs 6,500/-
7. Company. Purchase Airtel Recharge Voucher Rs 222/- from Goyal Sales.
8. Company. Received from Parth & Com. Rs- 84,500/-.
9. Company. Purchase Furniture of Rs. – 17,750/- From: – CASA Modern.
10. Company. Deposit Rs – 17,750 /- in ICICI Bank.
11. Company. Purchase Shares of Tata of Rs. 16,000/- in Cash.
12. Company. Withdraw Rs-23,750/- ICICI Bank.
13. Company Paid to Kanak Agency Rs. 65, 00/- Cash.
14. Company Paid to Goyal Sales Rs. 222/- Cash.
15. Company. Paid water bill Rs. 750/- & Electricity bill Rs. 4500/- in ICICI Bank.
16. Company. Paid to CASA Modern Rs -17,750/- in HDFC Bank.
Answer: – Net Loss 5472/-
Example 5
Create Company with following details:
Bala Ji Ent,
506, A B Road, Budhh Nagar (West) Mumbai-400068.
1. Company. Has toward bank Account’s their Opening Balance is
(A) SBI Bank – 1, 50,000/-
(B) Bank of India – 70,000/-
2. Company. Has Opening Cash Balance is Rs. – 2, 00,000/-.
3. Mr. Ashutosh is the owner of the company the opening Capital balance is 2, 75000/-.
4. 1-4-2016 – Company. Deposited cash in to SBI Bank – Rs 10,000/-.
5. 2-4-2016 – Company. Deposit cash in to Bank of India – Rs 15,000/-.
6. 2-4-2016 – Company. Deposit cash in to SBI Bank – Rs 17,000/-.
7. 31-4-2016 – Company. Deposit cash in to Bank of India – Rs 18,000/-.
8. 31-4-2016 – Company. Withdraw cash from SBI Bank – Rs 20,000/-.
9. 31-4-2016 – Company. Withdraw cash from Bank of India – Rs 10,000/-.
10. 1-5-2016 – Company Purchase Computer Table from Decor India Rs 7,500/-.
11. 1-5-4-2016 – Company Purchase Hero Honda Splendour plus from Chambal Motor’s Pvt. Ltd. Rs 48,000/-.
12. 1-5-2016 – Company. Purchase Stationary from Gautam Book Store Rs 9,750/-.
13. 22-4-2016 – Company. done Maintained work from Anurag Service Center of Rs.1250/-.
14. 24-4-2016 – Company. Paid to Decor India of Rs 7,500/- from Bank of India.
15. 26-4-2016 – Company. Paid to Chambal Motor’s Pvt.Ltd. Rs 48,000 from SBI Bank.
16. 30-4-2016 – Company. Paid to Gautam Book Store Rs 9,750/ from Bank of India.
Answer: – Net Loss 9750/-











